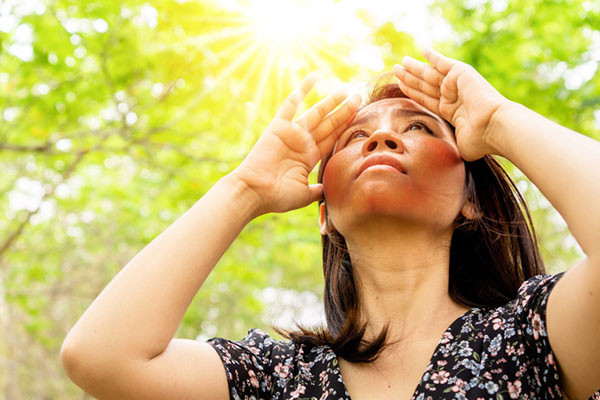
No one is truly allergic to the sun, but some people are quite sensitive to different types of sun rays and may develop mild to serious reactions after spending time in the sun.
There are several types of “sun allergies,” but polymorphous light eruption (PMLE), an autoimmune condition in the skin that occurs after sun exposure, is one of the most common. Other conditions considered as sun allergies are solar urticaria (hives and reddish patches that usually start 30 minutes to two hours after the sun exposure), actinic prurigo (papules and nodules that are intensely itchy on sun-exposed skin areas), and photoallergic reaction (when the UV rays from the sun modify the chemical structure of medications or products applied to the skin, and a person develops an allergy to the newly modified substance).
What causes PMLE?
People who have PMLE have immune cells that are triggered by sun rays, which attack their skin, and they develop a skin reaction to the sun’s the ultraviolet (UV) rays.
PMLE represents 70% of all sun-induced skin eruptions. It can affect both sexes and all skin types, and it usually starts when someone is a teen or young adult. PMLE may be an inherited condition. Being a female, having fair skin, and living in the north are other risk factors.
PMLE is more common in young women who live in temperate climates. People who live in temperate climates spend all winter out of the sun, so when it becomes warmer the sun exposure is intense. People who live in warmer climates are desensitized because they have a higher sun exposure all year.
What does PMLE look like?
PMLE can appear several hours or days after the first major sunlight exposure of the season, usually during spring or at the beginning of summer. The areas of the body generally affected the most are the ones that are covered during wintertime, but not in the summer: the neck, the chest, and the outer parts of the arms.
After exposure to the sun, people with PMLE usually notice reddish patches on their skin. These spots may itch, burn, or sting, but they typically don’t leave a scar. In more severe cases, the patches cover most of the body and may also be associated with headaches, fevers, tiredness, and low blood pressure. (If you experience these symptoms, see an urgent care provider for evaluation.) If you think you have PMLE or another sun allergy, a dermatologist is the best doctor to evaluate and treat your skin condition.
Does PMLE get better?
PMLE lesions often get better in approximately 10 days, and it’s important to avoid sun exposure until you are healed. People who develop PMLE can experience significant discomfort and have their life negatively impacted during the spring and summer months. However, repetitive sun exposure can make PMLE less likely to occur. The hardening effect, as it is called, means that the skin lesions that appear after the first episode are less severe, and they can be better tolerated during subsequent episodes.
What are current treatments for any sun allergy, including PMLE?
The best treatment is to prevent sun exposure. Avoid sunlight when it is most intense (from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.), and use UV-protecting clothing or clothes made of darker and thicker fabrics, as they will prevent the UV rays coming from the sun from reaching your skin. Hats with a wide brim protect your scalp, face, and (partially) the neck.
Broad-spectrum sunscreens that protect your skin from both UVA and UVB rays should be used daily, even if it’s cloudy. Apply sunscreen on your face and any part of your skin that is not covered by a hat or clothing. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, and if you go swimming or get sweaty reapply more frequently (water-resistant sunscreen should also be reapplied).
If you develop PMLE, the areas of skin impacted can be treated with steroid creams. In severe cases, your doctor may recommend a short course of steroid pills. Medications that reduce the immune response, such as azathioprine, are options for treating PMLE, since it is an autoimmune condition (the body is attacking it is own healthy cells).
Antihistamines are medications typically used for allergies that may help shorten the duration of reddish patches that itch or burn, and they also reduce inflammation.
Hydroxychloroquine (a medication also used to treat malaria) can be used in case of flare-ups, or as a prevention method when people travel to sunny locations during winter vacations.
Oral Polypodium leucotomos extract, a natural substance derived from tropical fern leaves, may work as a potent antioxidant, and has anti-inflammatory properties that are beneficial in the prevention of PMLE. Other nutritional supplements containing lycopene and beta-carotene (vitamin A derivatives) have a similar effect. A dermatologist will guide you on the best way to use these medications.
The bottom line
Sun allergies are common in temperate climates, but with a dermatologist’s guidance, vigilant sun prevention, and medications they can be managed throughout the sunny months of the year.
About the Authors

Neera Nathan, MD, MSHS, Contributor
Dr. Neera Nathan is a dermatologist and researcher at Massachusetts General Hospital and Lahey Hospital and Medical Center. Her clinical and research interests include dermatologic surgery, cosmetic dermatology, and laser medicine. She is part of the … See Full Bio View all posts by Neera Nathan, MD, MSHS 
Lais Lopes Almeida Gomes, Contributor
Dr. Lais Lopes Almeida Gomes is a dermatology research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital, and a pediatric dermatologist in Brazil. Her clinical and research interests include atopic dermatitis and global health. She is part of the … See Full Bio View all posts by Lais Lopes Almeida Gomes